1. Advantages of CHNZBTECH Water-Cooled Cables
Water-cooled cables are designed to carry extremely high electrical currents while maintaining safe operating temperatures. Their main advantages include:
• Very high current-carrying capacity
Water-cooled cables can safely transmit tens of kilo-amperes due to continuous heat removal by circulating water.
• Compact design
Compared with air-cooled conductors, water-cooled cables require much less installation space for the same current rating.
• Low operating temperature and long service life
Efficient cooling prevents copper overheating, reduces insulation aging, and ensures stable electrical performance.
• Excellent flexibility
Fine stranded copper conductors allow frequent movement, making these cables ideal for tilting furnaces and moving equipment.
• High copper quality
CHNZBTECH water-cooled cables use high-quality copper conductors.
The electrical resistivity at 20°C is only 43 µΩ·m, ensuring very low electrical loss and excellent current-carrying performance.
Forged copper cable terminals are applied, providing high mechanical strength, low contact resistance, and reliable long-term operation under high current conditions.

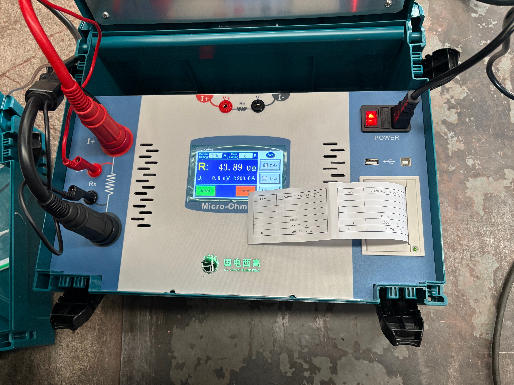
• Large section experience
For Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) applications, CHNZBTECH water-cooled cables are designed for furnaces up to 350 tons capacity.
The maximum conductor cross-sectional area for EAF cables is 7,500 mm², ensuring safe and stable transmission of extremely high currents.
For Ladle Furnace (LF) refining applications, the maximum conductor cross-sectional area is 6,500 mm², fully meeting the requirements of secondary refining operations.
2. Where Water-Cooled Cables Are Used in Industrial and Furnace Applications
Water-cooled cables are widely used in high-current and high-temperature industrial environments.
Typical furnace applications include:
• Induction furnaces (coreless and channel type)
• Electric Arc Furnaces (EAF)
• Ladle Furnaces (LF)
• ESR and VAR furnaces
3. Types of Water-Cooled Cables and Application Selection
Different furnace conditions require different types of water-cooled cables.
Flexible Hose-Type Water-Cooled Cable
Structure:
• Fine stranded copper conductor
• Internal water channel
• Rubber or silicone outer hose
Typical applications:
• Induction furnaces
• Tilting furnaces
• Movable transformer connections
This type is the preferred solution for induction furnace systems.
4. Working Principle of Water-Cooled Cables Under High Current Loads
When high current flows through the copper conductor, electrical resistance generates heat (I²R losses). Cooling water flows directly inside or around the conductor and absorbs this heat.
The heat transfer process includes:
• Heat conduction from copper to water
• Convective heat removal by flowing water
• Discharge of heated water to a cooling system such as a cooling tower or heat exchanger
Key operating parameters include water flow rate, inlet temperature, pressure, and allowable temperature rise. With continuous water flow, the cable temperature remains stable even under heavy current loads.
5. Why Induction Furnaces Require Water-Cooled Cables
Induction furnaces operate at low voltage and extremely high current levels. Air-cooled conductors would require very large cross-sections and still risk overheating.
Water-cooled cables are essential because:
• They safely carry very high current
• They support continuous melting operations
• They withstand strong electromagnetic forces
• They allow compact layout and furnace movement
Without water-cooled cables, stable and safe operation of induction furnaces would not be possible.
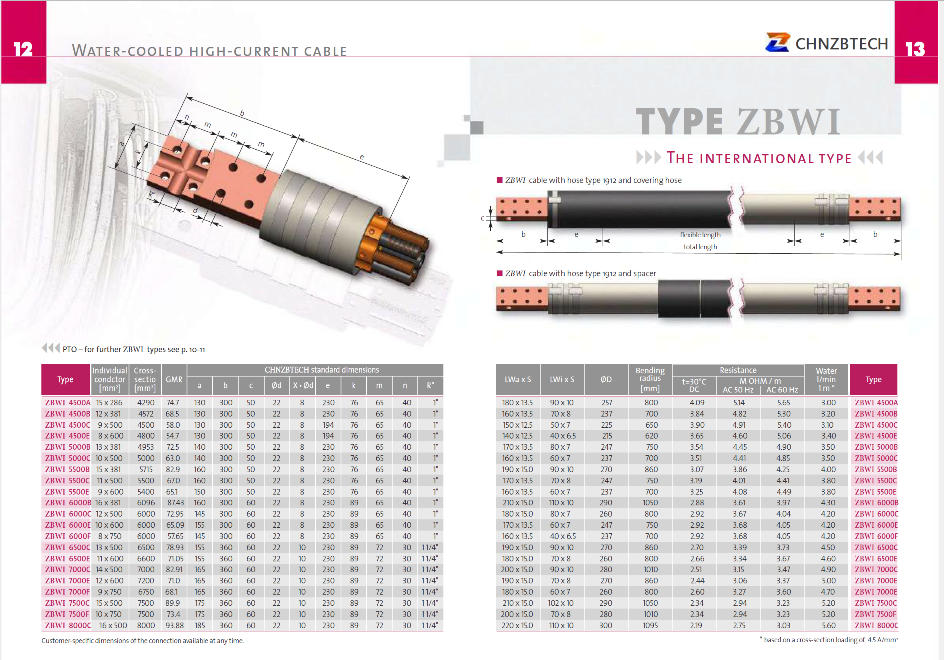
6. Technical data of water-cooled cable
Zhao Lianggang
Mr. Zhao, a graduate of Shaanxi Normal University, is an expert in metallurgical and steel equipment. With a robust knowledge of EAF, LF, VD/VOD, CCM, and related processes, he possesses a deep understanding of industry trends and customer needs. As a co-founder of CHNZBTECH, he leads the company's international strategy, expanding operations into over 20 countries across the Middle East, Southeast Asia, Africa, and South America. By merging his metallurgical expertise with global market insights, he has driven significant overseas growth and solidified the company's competitive position in the international metallurgical equipment industry.
 back homepage
back homepage

 EN
EN
 fr
fr  ar
ar  fa
fa